Osteochondrosis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system. According to statistics, about 90% of the population suffers from it. Most patients are not even aware of this, because the initial forms of the disease develop asymptomatically.
Another part of people only periodically feel discomfort in the back area, dismiss it as fatigue and do not receive treatment. Among all types of osteochondrosis, damage to the cervical spine prevails. If the treatment is started on time, there is a possibility of eliminating the disease.
The essence of osteochondrosis
There are two mechanisms involved in the development of osteochondrosis: dystrophic and degenerative. The first involves a violation of the trophism (nutrition) of the intervertebral cartilage (discs). The second is a consequence of dystrophy - organic changes in the structure of the cartilage tissue and vertebrae.
The essence of the disease is as follows: circulatory disorders in certain areas of the back lead to exhaustion and dehydration of cartilage tissue. Along with the liquid, it loses its nutritional components. As a result, the cartilage loses its elasticity and firmness, it sags. The distance between the vertebrae decreases, their statics (constancy of position) is violated. They can move and snuggle with each other, while pinching the nerve roots.
With osteochondrosis, cartilage wears down at an accelerated rate.
If the dystrophy persists, the muscles that support the spine also lose tone. The vertebrae sag even more. Due to increased friction, bulges develop - damage to the cartilaginous capsule with the bulge of its contents outward.
The spine's natural defense mechanism is then activated. Bony growths appear: osteophytes. They must ensure a stable position of the vertebrae. However, osteophyte growth often goes beyond "need". Overgrown growths also put pressure on cartilage debris and nerve fibers. Plus, they are solid. The spine loses its elasticity, the "adjacent discs" can be damaged. The patient loses mobility, suffers severe pain. The result of advanced osteochondrosis is disability.
Due to blood congestion, osteochondrosis is accompanied by the deposition of salts in areas adjacent to the cartilage. Such "accumulations" aggravate the development of the disease, accelerating damage to cartilage and vertebrae.
Why do you injure your neck more often?
The cervical spine is the most sensitive and fragile. Its elements are the smallest and are not adapted to heavy loads. However, the neck muscles do not participate in all types of physical activity. Hence the chronic blood congestion and malnutrition of the vertebral joints. If a person does not play sports, the risk of cervical osteochondrosis increases significantly. Most people rarely use their necks for mundane tasks.
The main cause of osteochondrosis is a hypodynamic lifestyle. Lack of exercise combined with passive leisure leads to muscle weakness and disorders of vascular tone. Neck disease causes prolonged stay in one position. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is considered a large number of office and computer workers.
Excessive physical activity causes muscle hypertonia. Being constantly in a state of tension, they also cause stagnant processes. Indirect causes of the disease include improper nutrition (excess salts and fats in the diet), metabolic disorders. The disease can be caused by autoimmune processes, lack of nutrients (vitamins and minerals), endocrine diseases and psycho-emotional shocks (since they are also accompanied by muscle overexertion).
How to recognize cervical osteochondrosis
Early osteochondrosis does not manifest itself in any way. In the 1st stage of development, cartilage becomes dehydrated. It is not noticeable from the outside, it does not cause physical discomfort. The disease can be discovered by chance, by examining the spine for injury or other discomfort.
In stage 2, the cartilage sags. Its height decreases, its repayment capacity deteriorates. The first symptoms may appear at this stage. Its characteristic is periodicity. The discomfort in the neck is clearly felt and then disappears. Periodically disappears completely. Sometimes a person feels pain in the neck. They appear after physical exertion or a prolonged stay in a position (sitting or standing). The unpleasant sensations appear in the morning, as the patient "walks", they weaken and remember themselves in the late afternoon. If salts are deposited in the cervical region, a person hears a cracking sound in the spine when turning. "Clicking" when tilting the head does not hurt.
In Stage 3, nerve roots can become partially trapped. This is accompanied by strong painful sensations. Patients complain of lumbago and sudden, sharp pain in the neck. Discomfort occurs after a static position. Unlike the early stages, you worry more often. A person's neck "gets tired" in no time. There may also be aching pains. They attack the patient in the afternoon and at night.
Congestion in the cervical spine causes a stroke. It is manifested by headaches (sometimes migraines), tinnitus, dizziness. With persistent hypoxia (lack of oxygen) there is a feeling of "goose bumps" on the scalp, often on one side. There are also secondary symptoms: the patient quickly tires, feels weak, drowsy (for no apparent reason), sometimes sleep is disturbed.
In parallel with the listed symptoms, the mobility of the joints in the cervical spine changes. Some head or neck movements are accompanied by sharp pain. The patient unconsciously reduces his amplitude, trying to maintain a comfortable position.
Stage 4 of osteochondrosis is accompanied by lumps and the appearance of osteophytes. Nerve root infringement leading to persistent pain syndrome. If inflammation develops in the process of changes, the pain becomes permanent. A person has more and more headaches, visual impairments (deterioration of vision in the evening, "flies", blurred image). Neck mobility is significantly limited. The patient avoids turning the neck, if necessary, turns the whole body. When nerves are damaged, pain, "goose bumps, " or numbness of the shoulder blades, shoulders, forearms, and even hands occur.
Diagnosis
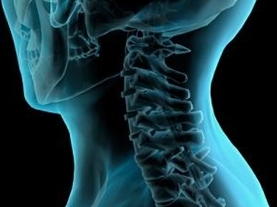
Above complaints should be directed to a neurologist, orthopedist, or vertebrologist. The doctor will interview the patient, conduct an examination. During the examination, he will check the sensitivity of the points, reflexes, mobility of the cervical spine. If osteochondrosis is suspected, an additional examination will be prescribed. Includes an X-ray of the cervical spine in several views.
If there are no specific abnormalities on the X-ray, but the patient still has complaints, an MRI or CT scan is prescribed. With these methods, osteochondrosis can be detected even in the earliest stages.
How to be treated
Even if the patient has all the signs of osteochondrosis, it is better to consult a doctor. Only a specialist can objectively assess the scale of destruction, distinguish chondrosis from other diseases, make the correct diagnosis and individually select a treatment regimen.
This disease takes a long time to develop. Exacerbations of osteochondrosis can occur periodically and go away on their own. The patient has yet to be examined.
The illness is treated on an outpatient basis. Surgical intervention (to remove osteophytes) is an extreme measure, resorted to only for severe damage to the nerve roots with severe pain syndrome. Conservative treatment can almost always be dispensed with.
Osteochondrosis (depending on the stage) is treated for 1 to 3 months. Therapy must be comprehensive. Medications alone are a must here. Even after the onset of improvement, the patient must monitor his activity and take preventive measures. The main task of treatment is to stop degenerative processes. Relieving symptoms with medication relieves the patient's condition for only a time. There are several ways to treat osteochondrosis at home.
Drug therapy
With the help of drugs, you can eliminate inflammation, relieve pain, provide the body with useful substances, and improve the nutrition of the cartilage of the cervical spine. Analgesics are used as a symptomatic treatment. In the inflammatory process, pain is eliminated with the help of NSAIDs. Medications are prescribed in the form of tablets (if symptoms are moderate) or injections (if pain is severe).
To eliminate muscle hypertonicity, muscle relaxants are prescribed in parallel with NSAIDs. These funds enhance the effect of painkillers, providing their "free access" to the focus of inflammation. Pain relievers are used in the shortest possible course (5-10 days) due to the risk of side effects.
Chondroprotectors are prescribed to increase elasticity and restore cartilage. In the acute period, these are injections. Doctors recommend long-term (3-6 months) intake of capsules or tablets as maintenance therapy.
To increase the effectiveness of the treatment, taking pills can be combined with the use of external agents (ointments, gels, patches). Pepper or menthol patches, pain relieving ointments, will ease severe pain. Also, osteochondrosis can be treated with chondroprotective ointments.
To improve the trophism of the joints, B vitamins and vascular preparations are prescribed.
Folk remedies

In the recipes of traditional medicine there are many recommendations for the treatment of osteochondrosis. As with the traditional approach, home remedies can be used internally or externally.
More powerful topical mixes:
- Horseradish compress.Horseradish root is rubbed with a fine grater, the porridge is spread on gauze, applied to the neck, covered with a film, wrapped with a bandage, left for 2 hours, washedwith clean water, the procedure is carried out 10 days in a row before bedtime.
- Compress with potatoes.Rub 3 large potatoes, add 1 tablespoon of honey and 1 tablespoon of mustard, spread the mixture on gauze and stick on the sore area for 1 hour, apply a compress 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
- Red pepper lotions.2 pods of hot red pepper are crushed into a mush, mixed with chopped aloe leaves, poured with a glass of alcohol, a day later, a gauze is moistened in the mixture, applied to the neck for15-20 minutes and wash off with cold water. The treatment lasts 2 weeks.
Mustard and pepper compresses are good for increasing blood circulation.
Inside you can take infusions, decoctions and tinctures. All recipes are aimed at normalizing metabolism, eliminating salts and eliminating inflammation:
- Parsley broth.3 tablespoons of parsley seeds are ground in a coffee grinder. Pour the mass with a liter of boiling water, cook over low heat for 10-15 minutes. After completely cooling, filter. It is taken orally 100 ml 2 times a day for 15 days.
- Barberry tincture.10 g of a mixture of dried roots and barberry bark (available at a pharmacy or herbalist) are poured into 100 ml of alcohol or vodka. The mixture is placed in a dark place for 10 days. After exerting yourself, take 30 drops orally three times a day half an hour before meals.
- Celery infusion.Pour a tablespoon of grated celery root with a liter of water. Bring to a boil over low heat, turn off immediately. After a day, filter, take 3 tablespoons before meals three times a day. The treatment lasts 1 month.
Before using any traditional medicine, you must make sure that you are not allergic to its components. If, when using compresses, a strong burning sensation occurs, you need to remove the bandage and rinse the remaining mixture under running water.
Physical therapy, exercise therapy and massage
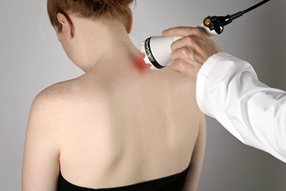
Physicians often prescribe physical therapy to treat osteochondrosis. It can be heating with medical ultraviolet light, exposure to low-frequency currents, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis or phonophoresis. Such manipulations are carried out in a hospital, using special equipment. They eliminate inflammation and improve drug access to cartilage tissue. The combination of medications and physical therapy can quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms. The course will require 10 to 15 procedures. To obtain a stable result, all types of physical therapy must be completely completed (not interrupted).
Physical therapy exercises for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck include simple exercises. They can be performed independently in the morning and evening, as well as between jobs. Physical education can be done sitting or standing.
The following exercises can be included in the exercise for cervical osteochondrosis:
- For 2 minutes, turn your head first clockwise and then counterclockwise (2 sets);
- gently lower your head forward, backward and to the side (15 times in each direction);
- raise the shoulders as high as possible, leaving the neck and head immobile (15-20 times);
- rotate the shoulders forward or backward, keeping the neck and head still (1 minute in each direction);
- fold the palms of the hands, pressing the fingertips in the center of the forehead, gently pass through the temporal regions, along the neck, up to the clavicles (10 times);
- without changing the position of the chin, gently bring the neck back (with the chin inward), then forward, to the sides (without tilting or turning the face);
- clasp your palms behind your back, pull your arms back, lift and stretch your neck as high as possible, stay in an extended position for 15 seconds (3 times).
For osteochondrosis, massage is considered the best way to improve blood circulation in the neck. It is best if the patient undergoes a full course (10-15 sessions) with a trained specialist. If this is not possible, you can knead your neck yourself at home.
Self-massage Quick Start Guide:
- first, the neck muscles should be warmed up: the nape area is rubbed with the fingertips or the edge of the palm;
- kneading involves gentle pressure followed by muscle relaxation: kneading with 4 collected pads and a thumb;
- lightly pinch the skin on the neck to improve blood circulation;
- pressing lightly with your finger on both sides of the spine, pass along the entire cervical region;
- To relax the back of the head, tap gently with your palm or fingers.
Each stage of the massage ends with a gentle caress with the palm. To enhance the effect, the neck is massaged with ointment. After the massage, you need to make sure that the cervical region is warm.
Massage your neck only with your palms or fingertips (not your fist).
All methods of treating osteochondrosis should be supplemented by diet. A classic healthy diet involves the use of lean meat, fish, shellfish, whole grains, and lots of vegetables. Food should be boiled, baked, or steamed.
During the entire period of the diet, it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt consumed, give up fast food and sweets. It is important to drink at least 1. 5 liters of water a day. It is useful to eat jellies and jellies to strengthen the joints.
With an integrated approach, the symptoms of the disease will disappear in a week and the destruction of the cartilage will stop completely.



































